Bitumen vs Polymer Modified Bitumen: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
In the road construction and waterproofing industries, selecting the right binder is critical to ensure durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Bitumen and Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB) are two widely used materials, each offering distinct advantages. This guide provides an in-depth comparison of their properties, manufacturing processes, performance characteristics, and applications to help stakeholders make informed decisions.
Understanding Bitumen
What is Bitumen?
Bitumen is a viscous, black, semi-solid form of petroleum derived during the refining of crude oil. It serves as a binder in asphalt mixtures and waterproofing products.
Key Properties of Bitumen
- Adhesion: Excellent bonding with aggregates.
- Waterproofing: Impermeable to water penetration.
- Thermoplastic Behavior: Softens upon heating and hardens when cooled.
- Viscosity: Dependent on grade and temperature.
Common Uses
- Road surfacing and paving
- Roofing and waterproofing membranes
- Industrial sealing and insulation
Understanding Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB)
What is PMB?
Polymer Modified Bitumen is conventional bitumen blended with polymers (e.g., SBS – Styrene Butadiene Styrene, or APP – Atactic Polypropylene) to enhance elasticity, strength, and thermal resistance.
Key Properties of PMB
- Improved Elasticity: Resists deformation under heavy traffic.
- Enhanced Temperature Tolerance: Maintains performance in extreme heat and cold.
- Longer Lifespan: Greater resistance to cracking, rutting, and fatigue.
- Customized Formulation: Tailored properties based on polymer type and dosage.
Common Uses
- High-traffic roadways
- Bridges and airport runways
- Roofing systems requiring high flexibility
- Waterproofing in extreme climates
Manufacturing Process Comparison
| Aspect | Bitumen | Polymer Modified Bitumen |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Crude oil refining residue | Bitumen blended with synthetic polymers |
| Processing | Heating and storage | High-shear mixing and homogenization |
| Cost | Lower | Higher due to polymer addition |
| Customization | Limited | High, based on polymer selection |
Performance Comparison
1. Temperature Susceptibility
- Bitumen: Susceptible to softening in high heat and cracking in cold weather.
- PMB: Reduced susceptibility due to enhanced thermal stability.
2. Rutting Resistance
- Bitumen: Adequate for low to medium traffic.
- PMB: Excellent, especially in heavy traffic zones.
3. Fatigue Life
- Bitumen: Moderate resistance to repeated load stress.
- PMB: Superior fatigue resistance, ideal for long-life pavements.
4. Aging and Oxidation
- Bitumen: Oxidizes over time, becoming brittle.
- PMB: Better resistance to oxidation and aging.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While PMB has a higher initial cost, its longer service life, reduced maintenance needs, and enhanced performance often make it more cost-effective over the pavement lifecycle.
Environmental Considerations
- Bitumen: Recyclable through reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP).
- PMB: Also recyclable, though polymer separation can be more complex.
- Use of warm-mix technologies can reduce emissions for both types.
Applications at a Glance
| Application | Preferred Binder |
|---|---|
| Rural Roads | Bitumen |
| Urban Highways | PMB |
| Bridges & Runways | PMB |
| Residential Roofing | Bitumen or PMB depending on climate |
| Extreme Weather Zones | PMB |
Decision-Making Flowchart
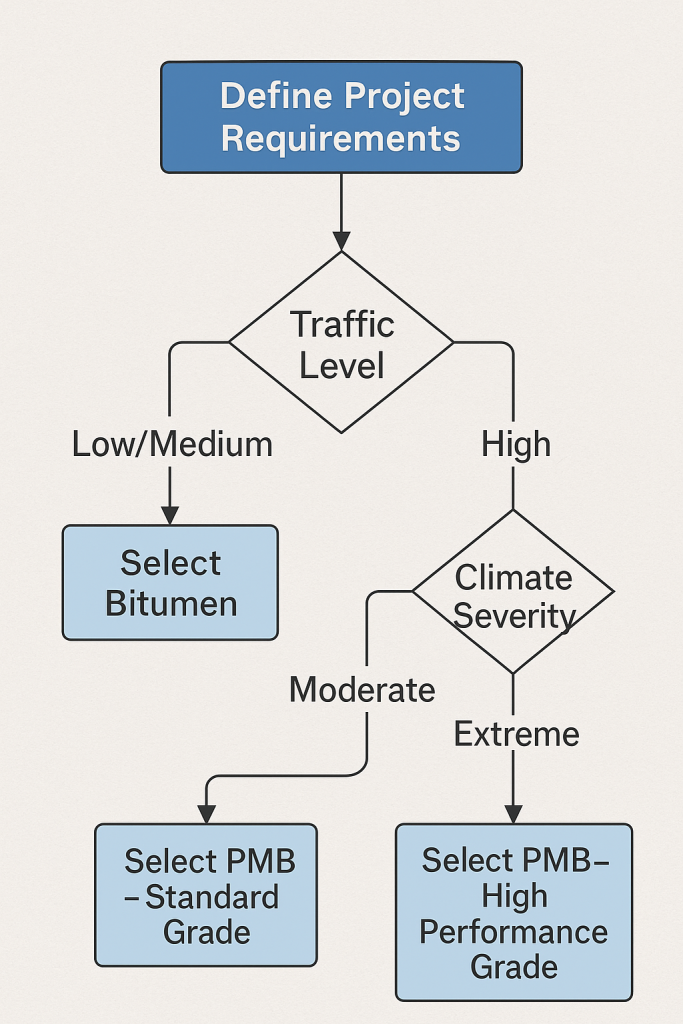
Conclusion
Bitumen remains a reliable, cost-effective solution for many applications, but when high performance under challenging conditions is required, Polymer Modified Bitumen delivers superior results. By evaluating project-specific factors such as traffic load, climate, and budget, engineers and project managers can choose the most suitable binder to ensure durability, safety, and value.
